|
If the ratio of N/2 is not
at an optimum value, then b decay will
occur. Within b decay a neutron changes
to a proton, or vice versa, leaving the mass number A
unchanged.
- A neutron-rich nucleus will change a neutron into a proton via b-
decay.
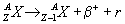
- A proton-rich nucleus will change a proton into a neutron via b+
decay.
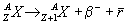
|
|