Recoil-Decay Tagging Studies at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland
Recoil-Decay Tagging Studies at the University of Jyväskylä, Finland
As our knowledge of the nuclear chart is extended to more
neutron deficient nuclei, the fusion-evaporation cross-sections for population
of these interesting nuclei are greatly reduced. Since the cross-sections for
competing reaction processes, such as fusion-fission, may be more than an order
of magnitude larger, it becomes increasingly difficult to extract the
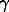 rays of interest from the high background
produced by the competing processes.
Fortunately, many of the neutron-deficient nuclei above 100Sn
decay by emitting charged particles (
rays of interest from the high background
produced by the competing processes.
Fortunately, many of the neutron-deficient nuclei above 100Sn
decay by emitting charged particles (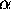 s,
s,
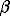 -delayed protons and direct protons) from their
ground states. Observation of these characteristic decay products gives a
signature that a certain nuclear species has been produced, and correlation
with the recoils associated with a given decay allows extraction of the
-delayed protons and direct protons) from their
ground states. Observation of these characteristic decay products gives a
signature that a certain nuclear species has been produced, and correlation
with the recoils associated with a given decay allows extraction of the
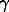 rays of interest. This technique is known as recoil-decay tagging.
rays of interest. This technique is known as recoil-decay tagging.
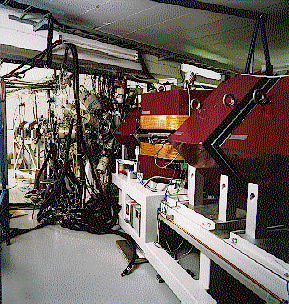
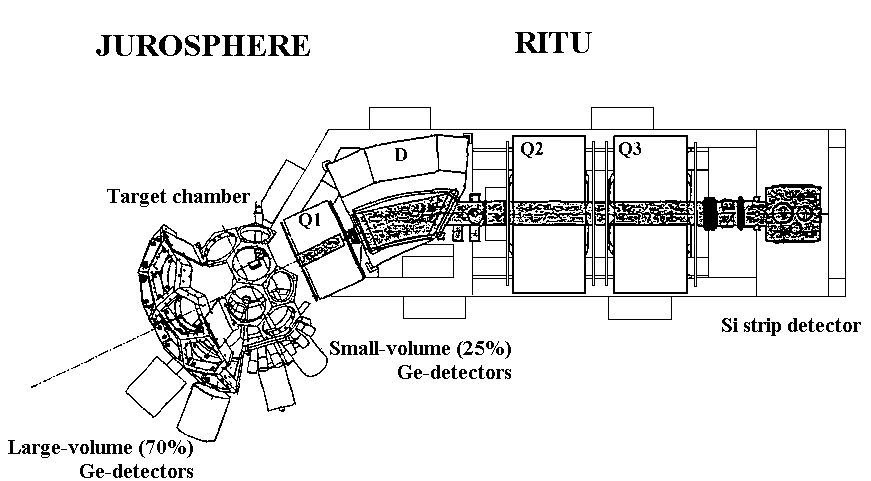
The JUROSPHERE + RITU Project
The
JUROSPHERE
+
RITU
project was a joint European collaboration, located at the
Accelerator Laboratory of the University of Jyväskylä, Finland,
for recoil-decay tagging studies of neutron-deficient nuclei. The
JUROSPHERE 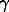 -ray array consisted of 10-15
Eurogam Phase I and 10 TESSA-type Compton-suppressed Ge detectors
(photopeak efficiency ~1.5% at 1.3 MeV) and was coupled to the RITU
gas-filled recoil separator. The RITU device magnetically separates
fusion-evaporation residues from unwanted products such as fission and
primary beam through their different magnetic rigidity. The transmission
efficiency through RITU is reaction-dependent and ranges approximately
from 10 to 50%. The system was commissioned on 11th March 1997, with
experiments involving over 80 collaborators from 22 worldwide institutions
running until 1st November 1997.
A schematic and photograph are shown here.
-ray array consisted of 10-15
Eurogam Phase I and 10 TESSA-type Compton-suppressed Ge detectors
(photopeak efficiency ~1.5% at 1.3 MeV) and was coupled to the RITU
gas-filled recoil separator. The RITU device magnetically separates
fusion-evaporation residues from unwanted products such as fission and
primary beam through their different magnetic rigidity. The transmission
efficiency through RITU is reaction-dependent and ranges approximately
from 10 to 50%. The system was commissioned on 11th March 1997, with
experiments involving over 80 collaborators from 22 worldwide institutions
running until 1st November 1997.
A schematic and photograph are shown here.
Prompt 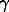 rays produced at the
target are collected by the JUROSPHERE germanium array, in coincidence with
fusion-evaporation products implanted into the RITU focal plane Si-strip detector.
Correlation of the implanted nuclear species to its subsequent decay allows
extraction of the coincident
rays produced at the
target are collected by the JUROSPHERE germanium array, in coincidence with
fusion-evaporation products implanted into the RITU focal plane Si-strip detector.
Correlation of the implanted nuclear species to its subsequent decay allows
extraction of the coincident 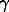 rays of interest.
rays of interest.
Highlights
- 168Pt and 170Pt levels identified for the first time
- 171Ir levels identified
- 176Hg levels observed up to 10+,
showing prolate intruder structure above 6+
- 184Pb excited states observed for first time beyond the mid-shell in the Pb isotopes
- 187Pb
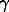 rays identified
rays identified
- 198Rn levels (up to at least 6+) for first time, with production cross-section of approximately 200 nb
- 201Rn levels identified for the first time
- 206Ra and 208Ra levels identified for first time
- 223Pa
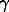 rays identified
rays identified
- 226U level scheme established for first time, showing evidence for octupole deformation
Back to Highlights Page
Last modified: 6 February 1998
Written by Paul Greenlees,
ptg@ns.ph.liv.ac.uk
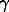 rays of interest from the high background
produced by the competing processes.
Fortunately, many of the neutron-deficient nuclei above 100Sn
decay by emitting charged particles (
rays of interest from the high background
produced by the competing processes.
Fortunately, many of the neutron-deficient nuclei above 100Sn
decay by emitting charged particles (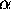 s,
s,
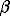 -delayed protons and direct protons) from their
ground states. Observation of these characteristic decay products gives a
signature that a certain nuclear species has been produced, and correlation
with the recoils associated with a given decay allows extraction of the
-delayed protons and direct protons) from their
ground states. Observation of these characteristic decay products gives a
signature that a certain nuclear species has been produced, and correlation
with the recoils associated with a given decay allows extraction of the
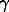 rays of interest. This technique is known as recoil-decay tagging.
rays of interest. This technique is known as recoil-decay tagging.

