|
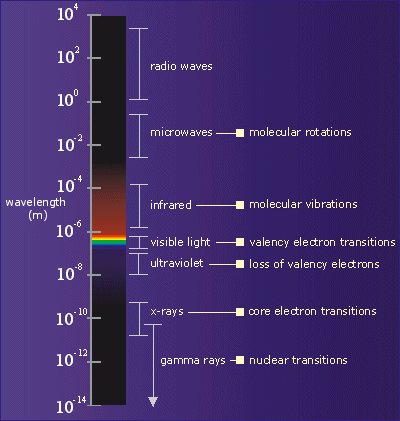 Gamma radiation
is electromagnetic in character. It sits at the high-energy (~103-105
keV), short-wavelength (~10-12m), end of the electromagnetic spectrum, shown
opposite. The phenomena responsible for different types of electromagnetic
radiation
are also detailed. Gamma radiation
is electromagnetic in character. It sits at the high-energy (~103-105
keV), short-wavelength (~10-12m), end of the electromagnetic spectrum, shown
opposite. The phenomena responsible for different types of electromagnetic
radiation
are also detailed.
Energy E,
wavelength l, and frequency n,
are related for electromagnetic waves by:
E =
h x
n and - l x
n = c
where h = Planck's constant
and
c = velocity of light
There is some overlap between higher energy x-rays and lower energy
gammas; different names are used merely to indicate their origin. |